Describe How Fish Use Their Muscles to Swim
D Their fur is thick and each hair is dense for better insulation. In many cases fish dedicate most of their mass to swimming muscles with internal organs like the heart and liver almost stuck to one side as an afterthought.
Movement of the fishs body in any plane causes movement of the fluid inside the canals.

. As a result a fish can bend the front part of its body in one direction while bending its tail in the opposite direction. A swimming fish is relying on its skeleton for framework its muscles for power and its fins for thrust and direction. Fish move their bodies from side to side as they swim whereas with dolphins all of the movement is up and downwards motion.
Fish use their back fin called ca u d al fin. Anguilliform in which a wave. Their gentle movement belies a complex flow of water that make these creatures highly energy-efficient swimmers.
They use some of their fins to propel themselves through the water and others to steer the body as they swim. It does not move in and of itself but acts as a point of stability for other bones. Some fish use specialized muscles around their buoyancy-modulating swim bladders to make noise.
The skeleton of a fish is the most complex in all vertebrates. This is a balloon-like. We have used blood flow tracers in swimming rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss to estimate the regional distribution of energy use across the myotomal and fin muscle groups to reveal the functional distribution of metabolic energy use within a swimming animal for the first time.
The faster the dolphin moves its tail up and down the faster it will propel itself through the water. Motion moves them forward through the. Suddenly two rapid bursts.
Other fishes like fast-swimming tunas move mostly with their caudal fin but use long thin pectoral fins for steering. Fish have a system of muscles for movement. A jellyfishs dome-shaped body or bell is made up of a solid jellylike substance covered by a thin layer of living cells.
The density of water makes it very difficult to move in but fish can move very smoothly and quickly. When we think of a swimming fish most of us associate with the majestic sweeping side-to-side movement of sharks and pelagic fast movers. Others might blow bubbles out their mouths or in the case of herring out their rear ends producing fish farts.
The epaxial muscles are the upper pair and the hypaxials are the lower pair see Fig. The mouth and stomach cavity are in the center of the bell surrounded by fleshy arms. The movement of the fluid causes the cupulae to move.
Fishes with wide pectoral fins like wrasses swim by flapping their pectoral fins. Their muscles on one side of the body while. Their movement through the water is similar to a snake moving on land.
Their skeletons and muscles work together to allow them to swim along with their fins and something called a swim bladder. The muscles open and close the bell drawing in water and then forcing it out again to push the. Herring mackerel and marlins pictured above.
Fish stretch or expand. In jawed fishes two major masses of skeletal muscle lieon each side of the fish divided by the horizontal connective tissue septum. Fish swim by flexing their bodies and tail.
Relaxing the muscles on other side. Their muscle is mostly brown to facilitate constant swimming and their fins are usually retracted as they are only used for turning. Eels and other snake-like varieties of fish swim by pushing themselves in a wave-like fashion through the water.
This is a relatively slow type of locomotion and a good deal of energy is needed to propel move the fish. Smooth Muscle A fishs smooth muscles work automatically. Skeletal muscle behind the head is uniformly segmental and is composed of shallow W-shaped myomeres.
It is concealed but its not safe. The jellyfish swims by contracting and relaxing a ring of muscles around the bell. Each myomere is controlled by a separate nerve.
They counteract the possibility of sinking with muscular effort reduced by decreasing drag and having a thinner cross-section -- both offered by the absence of the buoyancy device. Fish use the muscles on the sides of their bodies to push against the water in a similar manner to swim. Nevertheless red muscle seldom makes up even as much as 20 of.
Fish exhibit an s-shaped swimming pattern Bands of muscle along the body called myomeres drive this swimming motion rhythmic contractions Depending on the type of fish different fins may be used primarily for the forward movement. Skeletal muscles also move dorsal fins. Muscle contractions ripple through the body in waves from head to tail.
The jellyfish swims by contracting and relaxing a ring of muscles around the bell. Being well supplied with oxygen red muscle is used for steady constant-effort swimming and is found in active fish -particularly those that live in the open waters of seas and oceans. B They have massive webbed paws that make them excellent swimmers.
Using the Skeleton and Muscles The primary function of the skeleton is to aide movement of other parts. Most fish have a swim bladder. While the fastest fish swim at up to 70 miles per hour no human has ever managed even 4.
Most fish make such movements with their bodies to swim. When it comes to swimming fish demonstrate an effortless grace and power that humans can only dream of. Electric Eels Can Remotely Control Their Preys Muscles.
This is achieved in different groups of fish by a variety of mechanisms of propulsion most often by wave-like lateral flexions of the fishs body and tail in water and in various specialised fish by motions of the fins. The skull is the only truly fixed part of a fish. Back and forth.
These ampullae each contain the cupula. Fish use two strips of blood-rich red muscle - one on either. C They were hunted to the brink of extinction in the late 1800s.
The contractions whip the tail fin against the water to propel the fish through the water. Energy use by the myotomal muscle increased with speed to meet thrust. The major forms of locomotion in fish are.
A fish swims in the Amazon amid murky water and overgrown vegetation. Up to 24 cash back How Do Fish Swim. A They have small teeth and sharp claws which they use for prying and killing.
Fish locomotion is the various types of animal locomotion used by fish principally by swimming. When the cupulae move they press against sensitive hairs which in turn send electric impulses to the animals brain. Skeletal muscles are also attached to bones that move the fishs paired fins.
The real swimming action takes place in the jellys bell where muscles contract to expel water propelling the animal forward. Fish with streamlined bodies and a stiff crescent-shaped caudal fin or tail.

What Makes Fish Swim Fast Jstor Daily

Locomotion Twitter Search Twitter

Kinematics Of A Alternating And B Synchronous Pectoral Fin Download Scientific Diagram

Anatomy Of A Fish 2141094 Vector Art At Vecteezy
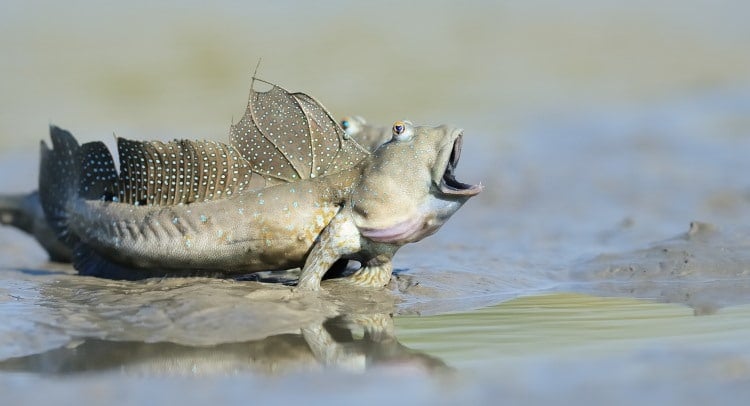

Fish Locomotion Movement 101 How Fish Swim Explained Earth Life
Fish Swim Bladder Animal Sea Life Rock Beauty Goldfish Transparent Png Pngset Com

Pdf Physiological Adaptations To Swimming In Fish

Fish Swimming How Do Fish Swim Dk Find Out

Pdf The Energetics Of Fish Swimming
How Do Fish Swim Practical Fishkeeping

Pdf Tuning In To Fish Swimming Waves Body Form Swimming Mode And Muscle Function Semantic Scholar

Can Fish Sense Hunger Low Oxygen And How Do They Swim Straight Motion Anatomy Resume Examples

Figure 1 From Forces On The Tail Surface Of Swimming Fish Thrust Drag And Acceleration In Bluefish Pomatomus Saltatrix Semantic Scholar
Which Body Part Helps Fish To Swim In Water Quora

Movement Of Fishes Interdependence Between Living Things Cbse Grade 5 Environmental Science Youtube


Comments
Post a Comment